Tag: Eczema
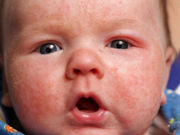
Clinical Scores Correlate Well in Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis
Clinical scores for sleep loss, pruritus correlate well with each other and with disease severity, QoL
Excimer Laser Efficacious for Chronic Hand and Foot Eczema
Reductions seen in average physician's global assessment scores, total lesion/symptom score
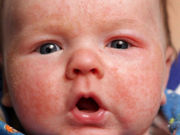
Early Weaning Linked to Reduced Risk of Atopic Dermatitis
Introduction of high number of different solid foods linked to reduced risk of atopic dermatitis
No Eczema Benefit to Partially Hydrolysed Whey Formula
Findings based on comparison to standard cow's milk formula in high-risk infants
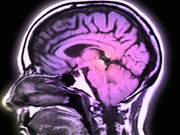
Allergies, Asthma, Eczema Tied to Lower Risk of Glioma
Researchers found 30 percent lower odds for those with respiratory allergies and eczema
Timing of DTaP Vaccine Not Tied to Food Allergies at Age 1 Year
However, delayed DTaP immunization is tied to a reduction in eczema
Pediatric Allergic Disease May Up Cardiovascular Risk
Findings held even after adjustment for obesity
Melatonin May Improve Sleep in Children With Atopic Dermatitis
Children taking melatonin fell asleep about 21 minutes sooner than those taking placebo
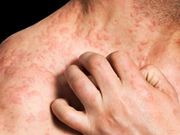
Smoke Exposure in Infancy Ups Sensitization to Food Allergens
Secondhand smoke exposure also linked to increased risk of eczema with sensitization
Ten New Gene Variants ID’d in Eczema Pathogenesis
Researchers say they now know of 31 gene variants linked to the skin condition