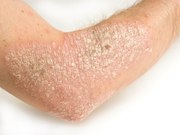
Case report: After initiation of ledipasvir-sofosbuvir, HCV RNA decreased, and skin lesions improved
WEDNESDAY, Jan. 17, 2018 (HealthDay News) — A case of remission of psoriasis after treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) has been described in a research letter published online Jan. 16 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Masaru Enomoto, M.D., from Osaka City University in Japan, and colleagues present the case of an 80-year-old man with a nine-year history of refractory psoriasis, with a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score of 8.3. The patient was treated with topical therapy with the corticosteroid clobetasol and the vitamin D3 analogue maxacalcitol; narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy was added. Even after topical therapy was replaced with betamethasone and the vitamin D3 analogue calcipotriol, the patient’s symptoms and signs persisted.
The researchers found that the patient had chronic HCV genotype 1b infection of unknown duration, and had not been treated for HCV infection. A 12-week course of ledipasvir-sofosbuvir was initiated. After initiation of ledipasvir-sofosbuvir therapy, the HCV RNA level decreased rapidly, became undetectable on polymerase chain reaction testing by week four, and remained undetectable for 24 weeks after completion of therapy. The skin lesions started to resolve gradually soon after initiation of ledipasvir-sofosbuvir therapy. The dose of topical agents and frequency of phototherapy were reduced and the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score decreased to 2.0.
“Here, we present what we believe to be the first report of a patient whose psoriasis improved when therapy with these agents was initiated,” the authors write.
One author disclosed financial ties to Gilead Sciences.
Copyright © 2018 HealthDay. All rights reserved.