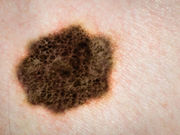
Researchers say skin cancer in these patients is likely due to more sun exposure
WEDNESDAY, June 15, 2016 (HealthDay News) — The small apparent increase in risk of melanoma in men prescribed phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors may be explained by greater sun exposure, according to new research published online June 14 in PLOS Medicine.
The new study included 145,104 men prescribed a PDE5 inhibitor. The investigators compared the men taking the medications to 560,933 men who didn’t use them.
The researchers found a slightly increased risk of melanoma in men who took the drugs compared to those who didn’t. There was evidence of a similar association between the use of PDE5 inhibitors and basal cell carcinoma and solar keratosis. The team also found strong evidence suggesting that men with a history of solar keratosis were more likely to become PDE5 inhibitor users.
“All of our observations pointed towards the small apparent increase in risk of melanoma in men prescribed PDE5 inhibitors being explained by greater sun exposure, rather than a side effect of the drugs themselves,” senior author Krishnan Bhaskaran, Ph.D., of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said in a journal news release.
One author disclosed financial ties to GlaxoSmithKline.
Full Text
Copyright © 2016 HealthDay. All rights reserved.